Rotary Die
Compared with flatbed die, the rotary die (or cylindrical die) cuts faster and works for more intricate products. Its application was earliest found in after-press area, and gradually reached into electronics, pharmaceutical, cosmetic and other industries. Especially in the electronics industry, as the increasing of the quantity and complexity of diecut pieces for mobile phones, computers, cameras and other multimedia devices, flatbed die cutting is no longer enough to meet market demand.
So, the rotary die has a large space for growth in this occasion. It has been through the development from the simple single-die cut to the multi-die cut, from simple material cut to a variety of special processing. The rotary die shows its incomparable advantages in achieving high efficiency while saving labor.
Rotary Die Design Elements
1. Gear
The relationship between gear teeth number and diameter:
The number of gear teeth varies with different diameters. Theoretical diameter = tooth number × modulus, for example: if the teeth number is 60 and the modulus is 1.01063, then the theoretical diameter is 60.636mm.
2. Drawing Compensation
Because the material being cut will deform under tension brought by the die cutting, so on the die drawing, we need to add a deformation counterbalance circumferentially and remove the same deformation amount axially.
| No. | Diameters /mm | Stretch Factor |
| 1 | 42-44 | 1.02 |
| 2 | 45-49 | 1.019 |
| 3 | 50-65 | 1.015 |
| 4 | 66-76 | 1.012 |
| 5 | 77-80 | 1.01 |
| 6 | 81-85 | 1.007 |
| 7 | 84-94 | 1.005 |
| 8 | 95 and above | 1 |
The above data are empirical values. In the case of special materials or products, the values are subject to actual situations.
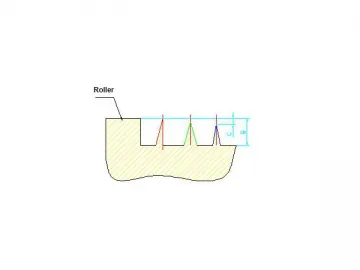
3. Blade Angle
Chisel blade (blade 1): a blade with one straight side, for cutting materials with higher trimming requirements, but may suffer edge chipping because of the small angle;
V blade (blade 2): a commonly used blade, the angles of the blade edge are same on both sides;
Asymmetrical V blade (blade 3): a blade that has edge sides in two inconsistent angles, for cutting materials with higher trimming requirements, and can better prevent edge chipping.
Please choose the right type of blade for the rotary die according to material thickness and hardness, as well as the cutting requirements.
4. Blade HeightBlade height: the height of the blade can be selected according to the thickness of the cut material, usually 1.2mm;Drop height: different drop heights can be designed for the same rotary die as needed.l
5. Blade Clearance
The blade clearance depends on the product design. Currently, the minimum clearance is possible to be 0.3mm. The smaller the clearance is, the shallower the processing depth will be. So, it is better not to use small clearances when cutting too hard or too thick products, otherwise the blade edge will be easily damaged.
How a Rotary Die Is Made
1. Material Preparation
Prepare raw material according to the size and requirement of the cutting die the customer needs.
2. Process Design
The production of rotary die is based on customers’ drawings. We will firstly confirm whether the drawing is workable, then plan the production process.
3. Lathe Rough Processing
The rough processing shapes the raw materials and gets them ready for the next grinding step. Engaged in this work, the worker must wear protective glasses to prevent iron pieces splashing into the eyes.
4. Grinder Rough Processing
This step of processing grinds the cylinder roughly and makes preparation for the CNC processing. It is prohibited to stand right in front of the grinding wheel to avoid injury caused by flying broken wheel pieces.
5. CNC Machining Center Rough Processing
The blade of the rotary die will be roughly made in this step, and be ready for precision machining. Engaged in this work, the worker should never have any part of the body go into the internal machine. Safety doors must be closed during cycled starts. Workers with long hair must wear a hat.
6. Heat Treatment
After vacuum heat treatment process, the die hardness can reach HRC 58-62 degrees.
7. Grinder Finishing
Blade height, drop height, shaft shoulder and shaft end are finely grinded for better smoothness. The size is guaranteed to be exactly in accordance with the drawing, with deviation of ± 0.002mm. The step means getting ready for CNC finishing. It is prohibited to stand right in front of the grinding wheel to avoid injury caused by flying broken wheel pieces.
8. CNC Finishing
The blade edge of the rotary die will be finished and ready for the angle refinement. Engaged in this work, the worker should never have any part of the body go into the internal machine. Safety doors must be closed during cycled starts. Workers with long hair must wear a hat.
9. By-Hand Carving
The blade edge will be zoomed out in 40-fold by microscope for angle refinement and glitch removal. Engaged in this work, the worker must be careful not to touch the edges to prevent cuts.
10. Test Cut
Drop height, smoothness, sharpness and waste removal effect of the rotary die will be tested. Engaged in this work, the worker should not get close to the rotating cutting tool and shaft to avoid hand being seized by the machine.
11. Quality Control
The quality control ensures that the size of the rotary die is in line with the drawing, and the cut trace as well as the cutting depth are correct. Engaged in this work, the worker should be careful not to touch the edges to prevent cuts.
12. Packaging
The finished rotary die will be cleaned, wrapped, and put into box together with the test cut report. The worker should be careful not to touch the blade edges to prevent cuts.
HADESHENG is a professional die cutter and cutting die manufacturer in China. Our products come in complete series and we offer the best die cut solutions.
Links:https://www.globefindpro.com/products/59774.html























