MINI-S Series Mini Variable Frequency Drive
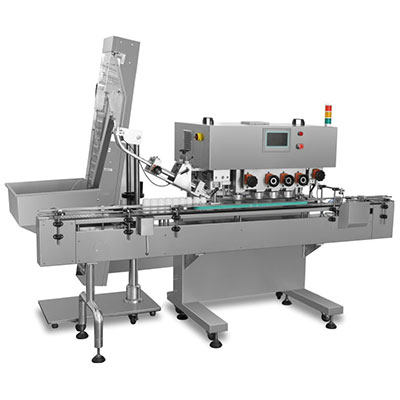
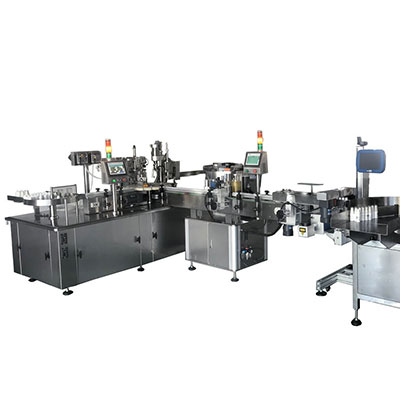
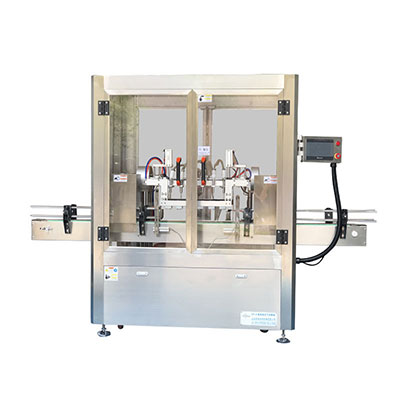
Housed in a black cover, our MINI-S series variable frequency drive features a compact design. The advanced control scheme allows this drive system to deliver a wide range of torques and speeds in a precise manner. For customers who go for ease of control, this low voltage variable speed drive might be your best bet as it allows for simple operation while delivering various functions.
Features of Variable Frequency Drive
1. Power Range: 0.75KW-1.5KW/220VAC
2. The intelligent power module, or IPM for short, houses inside all variable frequency drive parts in a compact design. It provides an easy way to cool the components thereby ensuring reliable operation.
3. Built-in PID controller, automatic sleep and wakeup functions, and 7 preset speeds.
4. Designed to allow wide-range voltage control, this adjustable-speed drive is quite effective with low-voltage tasks.
5. Assemblies are mounted onto a control board to provide a means of remote control. There is also a potentiometer fitted on the board to facilitate voltage adjustment.
6. Built-in braking unit provides powerful, reliable braking in most operating conditions. Users can refer to our instruction manual when selecting the braking resistor.
7. High-efficiency heat sink design, complete with variable frequency drive components protection.
8. A wide range of V/F curves is available for options.
9. Boards with conformal coatings
10. Programmable relay output generates up to 16 operational status signals.

Applications of Variable Frequency Drive
Typical uses of our variable frequency drive are in machinery, textile, printing and dyeing, packaging, food and medicine, reflow soldering, and OEM applications.
VFD Installation Size
| Specifications | W | W1 | H | H1 | H2 | D | D1 | D2 | D3 | R |
| MINI-S | 85 | 74 | 155 | 144 | 122 | 72 | 98 | 112 | 2.5 |
| MINI-S/L VFD | Specs | |
| Input | Rated voltage and frequency | Single-phase 220V, three-phase 220V, three-phase 380V; 50Hz/60Hz |
| Allowable variations (tolerance) | Voltage: -20% 20 Voltage unbalance: <3% Frequency: ±5 | |
| Output | Rated voltage | 0~200V /0~380V |
| Frequency range | 0Hz~400Hz | |
| Overload capability | 150% overload for 1 min, 180% overload for 1s, 200% overload (instant protection needed) | |
| Main control function | Control mode | Pulse-Width Modulation (PWM for short, using vector voltage for effective control) Sensorless vector control (SVC) |
| Frequency accuracy | Digital mode: Max. frequency ×±0. 01% Analog mode: Max frequency ×±0. 2% | |
| Frequency resolution | Digital mode: 0.01Hz Analog mode: Max frequency ×0.1% | |
| Torque rise | Automatic torque rise. Manual torque rise: 1%~30.0% | |
| V/F curve | Linear V/F, quadratic V/F curve, user-defined V/F curve | |
| S-curve acceleration/deceleration (S ramp) | Optional time units: minute/second Maximum Combined Time of Acceleration and Deceleration: 6000s (adjustable range: 0.1~3600s). | |
| DC brake | Optional part. Operating frequency: 0~20Hz Operating voltage level: 0~20% Operating time: 0~20s | |
| Jog switch | Jog Frequency range: 0.1Hz~50.00Hz Jog acceleration and deceleration time: 0.1s~3600s | |
| Built-in PID Controller | A closed loop control system is formed with the aid of PID, applicable for process control, like flow rate or pressure adjustment. | |
| Multiple preset speeds | The PLC system, together with control terminals, enables a number of operational speeds. | |
| Weave and wobble | Adjustable weave and wobble frequency | |
| Automatic voltage adjustment | When the mains voltage changes, the output voltage is kept constant by adjusting PWM output (AVR function). | |
| Power saving mode | V/F curve is optimized automatically to changing electric loads in an attempt to achieve maximum running efficiency. | |
| Automatic current control | Current-limiting features prevent the VFD control tripping on a fault caused by excess current. | |
| Sensorless vector control | Torque | 150% torque output at 1Hz Torque adjustment accuracy: 0.1% |
| Automatic display of motor parameters | Operators can get motor status data from the display screen when the variable frequency drive stops operating. | |
| Run Enable | Command channels | Control of operation modes Control of digital I/O ports Control of serial port |
Links:https://www.globefindpro.com/products/75437.html