Pipe Tee
The pipe tee is a kind of pipe fitting. It is directly butt welded with steel pipes. Divided according to the diameter, there are equal tee and reducing tee. The equal tee looks nice, has smooth surface and is resistant to acid, alkali as well as corrosion.
Product Information
| Executive Standard | GB/T12459, GB/T13401, ASME B16.9, SH340, SH3409, HG/T21635, HG/T21631, SY/T0510, etc. |
| Material | 304, 304L, 316, 316L, etc. |
| Working Pressure | PN0.25MPa, PN0.6MPa, PN1.0MPa, PN1.6MPa, PN2.5MPa |
Dimensions of Equal Tee
| Type | Nominal Diameter | Wall Thickness |
| Welded Type | DN250--DN1600 | 20-50mm |
| Seamless Type | DN15--DN500 | 20-50mm |
Specification of Reducing Tee
| Nominal Diameter (mm) | D×d (mm) | Nominal Pressure (MPa) | L (mm) | NominalDiameter (mm) | D×d (mm) | Nominal Pressure (MPa) | L (mm) |
| 80×65 | 89×76 | 2.5 | 94 | 200×125 | 219×140 | 2.5 | 179 |
| 100×65 | 108×76 | 104 | 200×150 | 219×159 | |||
| 100×80 | 108×89 | 200×150 | 219×165 | ||||
| 100×65 | 114×76 | 200×150 | 219×168 | ||||
| 100×80 | 114×89 | 250×150 | 273×159 | 215 | |||
| 125×65 | 133×76 | 122 | 250×150 | 273×165 | |||
| 125×80 | 133×89 | 250×150 | 273×168 | ||||
| 125×100 | 133×108 | 250×200 | 273×219 | ||||
| 125×100 | 133×114 | 300×150 | 325×159 | 245 | |||
| 125×65 | 140×76 | 300×150 | 325×165 | ||||
| 125×80 | 140×89 | 300×150 | 325×168 | ||||
| 125×100 | 140×108 | 300×200 | 325×219 | ||||
| 125×100 | 140×114 | 300×250 | 325×273 | ||||
| 150×65 | 159×76 | 142 | 350×200 | 377×219 | 1.6 | 305 | |
| 150×80 | 159×89 | 350×250 | 377×273 | ||||
| 150×100 | 159×108 | 350×300 | 377×325 | ||||
| 150×100 | 159×114 | 400×200 | 426×219 | 328 | |||
| 150×125 | 159×133 | 400×250 | 426×271 | ||||
| 150×125 | 159×140 | 400×300 | 426×325 | ||||
| 150×65 | 165×76 | 450×200 | 480×219 | 359 | |||
| 150×80 | 165×89 | 450×250 | 480×273 | ||||
| 150×100 | 165×108 | 450×300 | 480×325 | ||||
| 150×100 | 165×114 | 500×200 | 530×219 | 387 | |||
| 150×125 | 165×133 | 500×250 | 530×273 | ||||
| 150×125 | 165×140 | 500×300 | 530×325 | ||||
| 150×65 | 168×76 | 600×350 | 530×377 | ||||
| 150×80 | 168×89 | 600×200 | 630×219 | 441 | |||
| 150×100 | 168×108 | 600×250 | 630×273 | ||||
| 150×100 | 168×114 | 600×300 | 630×325 | ||||
| 150×125 | 168×133 | 600×350 | 630×377 | ||||
| 150×125 | 168×140 | 179 | 600×400 | 630×426 | |||
| 200×100 | 219×108 | 600×450 | 630×480 | ||||
| 200×100 | 219×114 | 600×500 | 630×530 | ||||
| 200×125 | 219×133 | - | - |
Forming Process
During the forming process, the tube billet, whose diameter is larger than that of pipe tee, is squashed to make its diameter approximate to the size of the needed product. Then, open a hole at the position of the branch tube. After being heated, the tube billet is placed into the forming die. Meanwhile, the stamping die for drawing branch tube is mounted into the tube billet. Under the action of pressure, the tube billet is compressed along the radial direction. During the compression process, the metal flows toward the branch tube direction and forms the branch tube with the drawing action of stamping die.

The whole process is formed through the radial compression of the tube billet and the drawing action at the position of branch tube. Different from the hydro-bulging technology, the metal of the branch tube of the pipe tee is compensated via the radial compression of the tube billet. Thereby, this kind of forming process is called radial compensation technology.
Because the pipe tee is produced by heating the tube billet first, the tonnage of the required equipment for material forming is reduced. The hot pressing technology has a wide adaptability for the materials like low carbon steel, alloy steel and stainless steel. The pipe tee with large diameter and thicker wall is generally fabricated by using such forming technology.
Links:https://www.globefindpro.com/products/84910.html
-
 DN Steel Jacketed Insulated Pipe
DN Steel Jacketed Insulated Pipe
-
 Coal Tar Epoxy Coated Steel Pipe
Coal Tar Epoxy Coated Steel Pipe
-
 Flange
Flange
-
 Pipe Bends
Pipe Bends
-
 19.5 Inch Aluminum Alloy Wheel
19.5 Inch Aluminum Alloy Wheel
-
 LSAW Steel Pipe (Longitudinal Submerged Arc Welding)
LSAW Steel Pipe (Longitudinal Submerged Arc Welding)
-
 HS38 Radial Ply Tire
HS38 Radial Ply Tire
-
 3 Layer PE Coated Steel Pipe
3 Layer PE Coated Steel Pipe
-
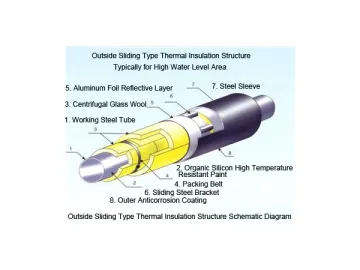 Prefabricated Insulated Pipe for Underground Installation
Prefabricated Insulated Pipe for Underground Installation
-
 API 5L Steel Pipe
API 5L Steel Pipe
-
 17.5 Inch Steel Wheel
17.5 Inch Steel Wheel
-
 Cement Mortar Lined Steel Pipe
Cement Mortar Lined Steel Pipe