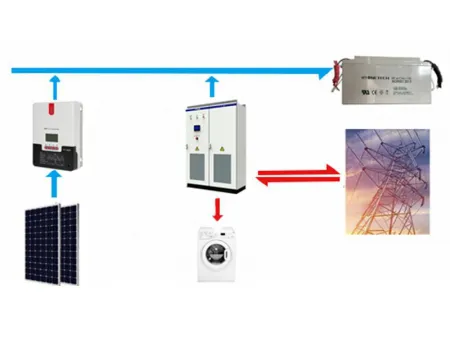
Residential & Commercial Hybrid Microgrid System
A Micro-Grid, also known as a microgrid, is a compact power generation and distribution system that consists of various components such as distributed generation, energy storage devices, energy conversion devices, loads, monitoring and protection devices. This system has the flexibility to operate in conjunction with an external grid or independently. Depending on the type of busbars utilized, Micro-Grids can be categorized into three types: DC microgrid (DC coupling), AC microgrid (AC coupling), and AC-DC hybrid microgrid.
Benefits of Residential & Commercial Hybrid Microgrid System
The microgrid system is able to take control of itself, offering protection and management with unparalleled precision. Not only is it a fully functional power system, but it has the unique capability of providing energy and ability to balance, optimize operations, detect and protect against faults, and manage power quality. This remarkable technology delivers the following advantages:
On-grid and off-grid systems designed specifically for residential users can make all the difference. Choosing the right photovoltaic module, controlling system circuits, managing loads, and optimally connecting to the grid and diesel generator, these are all essential elements for success. The EMS system enables efficient management of diesel generators, public power grids, batteries, photovoltaic modules, and wind turbines in order to provide a continuous, high-quality energy to whatever load is required, thus keeping user power usage stable. To ensure users have the power they need quickly, flexible networking corresponding to the site conditions is employed, utilizing either a DC or AC coupling scheme. By using these mature strategies, local consumption of new energy is enabled, which reduces user's expenses for cable laying and meets their power requirements efficiently. The powerful energy storage inverter and energy management system (EMS) form the core of the system, augmenting the cloud platform monitoring technology for operation and maintenance. Connected to the grid, this system can be deployed to a single machine or across multiple devices, assuring issues including grid expansion, three-phase balance, peak clipping and valley filling, seamless switching, and power quality, are all efficiently attended to. In this way, tailored and diverse user requirements are wholly satisfied. Applications Islands: The construction of renewable energy sources such as photovoltaic and wind power, along with energy storage systems, are essential to power islands - of the approximate 100,000 worldwide - in a sustainable and green way. Such solutions not only improve economic efficiency, but also reduce emissions of harmful pollutants and carbon, surpassing those of diesel power plants which are commonplace on some islands. By utilizing renewable energy sources and energy storage systems, islands can now enjoy sustainable electricity and a pollution-free environment. Mines and oil fields: In remote areas with no main grid access, mines and oil fields are largely dependent on either connecting to a new power grid or utilizing heavy oil and diesel to generate electricity. However, these costly options tend to sacrifice reliability and come with low power supply guarantees. Utilizing a solar microgrid, however, significantly reduces the cost of electricity while simultaneously dramatically increasing the reliability of power supply. For villages in remote areas, an independent microgrid provides an efficient way to power their homes when the large power grid isn't available or the cost of connecting is high. This microgrid can operate independently or be connected to the power grid, once the conditions are suitable for a local connection.Links:https://globefindpro.com/products/367.html
-
 Tapered Drill Rods
Tapered Drill Rods
-
 Wind Turbine
Wind Turbine
-
 Gel Battery & Lead Acid Battery
Gel Battery & Lead Acid Battery
-
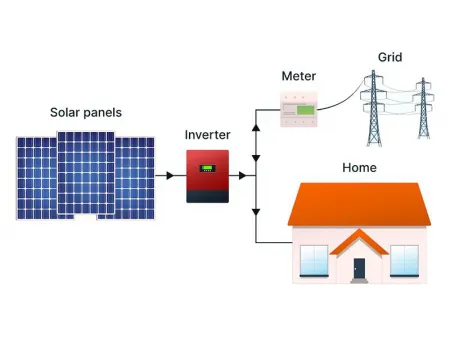 On-Grid Solar Power System
On-Grid Solar Power System
-
 Guide Tubes
Guide Tubes
-
 Solar Charge Controllers
Solar Charge Controllers
-
 Hybrid Power System
Hybrid Power System
-
 P2.97 Outdoor and Indoor LED Display Screen
P2.97 Outdoor and Indoor LED Display Screen
-
 Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery (LiFePO4 Battery)
Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery (LiFePO4 Battery)
-
 YT24 Air Leg Rock Drill
YT24 Air Leg Rock Drill
-
 12V/24V Solar Charge Controller (10A-100A)
12V/24V Solar Charge Controller (10A-100A)
-
 YT27 Air Leg Rock Drill
YT27 Air Leg Rock Drill