Heat Resistant Reforming Catalyst
The HHZ03Y heat resistant reforming catalyst is a new type of calcined thermal protection catalyst in the shape of Raschig ring, and its major active component is nickel oxide. The carrier is fabricated through calcination at elevated temperature of over 1500℃, thereby offering good resistance to deformation. Moreover, the large overall dimension ensures excellent heat storage property and heat shock resistance, while the nickel oxide realizes pre-reforming to some extent.

Advantage
As mentioned above, our nickel based reforming catalyst is in the form of Raschig ring, so it is not likely to change its position even under the impact of high speed gas flow. But, alumina spheres and porous spheres tend to move easily when high speed gas stream is fed, and this is a result of their mobility.
It has already been field-proven that catalyst beds will sink downward in the middle of their surface when using spherical reforming catalyst, and this is observed in most manufacturing plants, if not all of them. However, if our chemical fertilizer catalyst is adopted, most parts of the catalyst bed will be flat as ever when unloading catalyst.
Physical Property of Heat Resistant Reforming Catalyst
| Appearance | Dimension (mm) | Bulk density (g/ml) | ||
| OD | ID | Length | ||
| Grey, Raschig ring | 25 | 10 | 15 | 1.0±0.05 |
Major Chemical Composition of Heat Resistant Reforming Catalyst
| NiO | Al2O3 | CaO | SiO2 | Fe2O3 | Na2O K2O |
| ≥5.0% | ≥89% | ≤4.0% | ≤0.1% | ≤0.35% | ≤0.1% |
Technical Performance of Heat Resistant Reforming Catalyst
| Average radial crush strength (N) | Percentage of catalyst with crush strength lower than 300N (%) | Thermal stability (1.9kg for every catalyst at 1400℃) |
| ≥400 | ≤5.0 | No deformation or breakage |
Links:https://globefindpro.com/products/76955.html
-
 Energy Saving PET Sheet Extrusion Line
Energy Saving PET Sheet Extrusion Line
-
 Molecular Sieve
Molecular Sieve
-
 Activated Alumina
Activated Alumina
-
 Ammonia Decomposition Catalyst
Ammonia Decomposition Catalyst
-
 Methanation Catalyst
Methanation Catalyst
-
 Coal Mill
Coal Mill
-
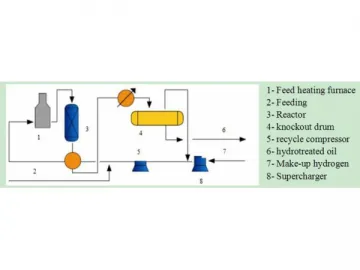 Light Distillate Hydrotreating Catalyst
Light Distillate Hydrotreating Catalyst
-
 Primary Reforming Catalyst
Primary Reforming Catalyst
-
 Maleic Anhydride Catalyst Carrier
Maleic Anhydride Catalyst Carrier
-
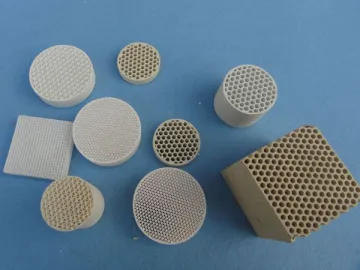 Honeycomb Ceramic Packing
Honeycomb Ceramic Packing
-
 Diesel Deep Hydrotreating Catalyst
Diesel Deep Hydrotreating Catalyst
-
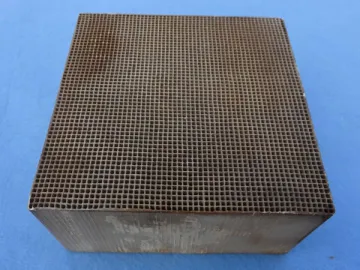 Exhaust Gas Purifying Catalyst
Exhaust Gas Purifying Catalyst











